Organizations face an increasing number of cybersecurity threats. As businesses embrace digital transformation, securing applications and data becomes more critical than ever. Microsoft Power Platform provides an innovative low-code solution to help organizations modernize their business applications while maintaining robust security and compliance measures.
The Growing Cybersecurity Challenge
Cybersecurity threats have become more sophisticated, targeting sensitive business data stored in enterprise applications. Traditional business applications often lack proper security controls, making them vulnerable to attacks such as data breaches, insider threats, and account impersonation.
Organizations must strike a balance between security and productivity — too many restrictions can hinder innovation, while insufficient security measures can lead to costly data leaks. Microsoft Power Platform helps address these challenges with built-in security capabilities, allowing businesses to develop applications without compromising security.
🔗 Learn more about cybersecurity best practices: Microsoft Cybersecurity
Key Security Challenges in Low-Code/No-Code Development
Low-code and no-code platforms democratize application development, enabling business users to build apps without extensive coding knowledge. However, they also introduce new security risks, such as:
- Account Impersonation
- Data Leakage
- Authentication Failures
- Misconfigured Security Settings
- Injection Attacks
- Weak Security Logging and Monitoring
To mitigate these risks, organizations must implement proper security policies, governance frameworks, and access controls within Power Platform.
🔗 OWASP Top 10 Low-Code Security Risks: OWASP Report
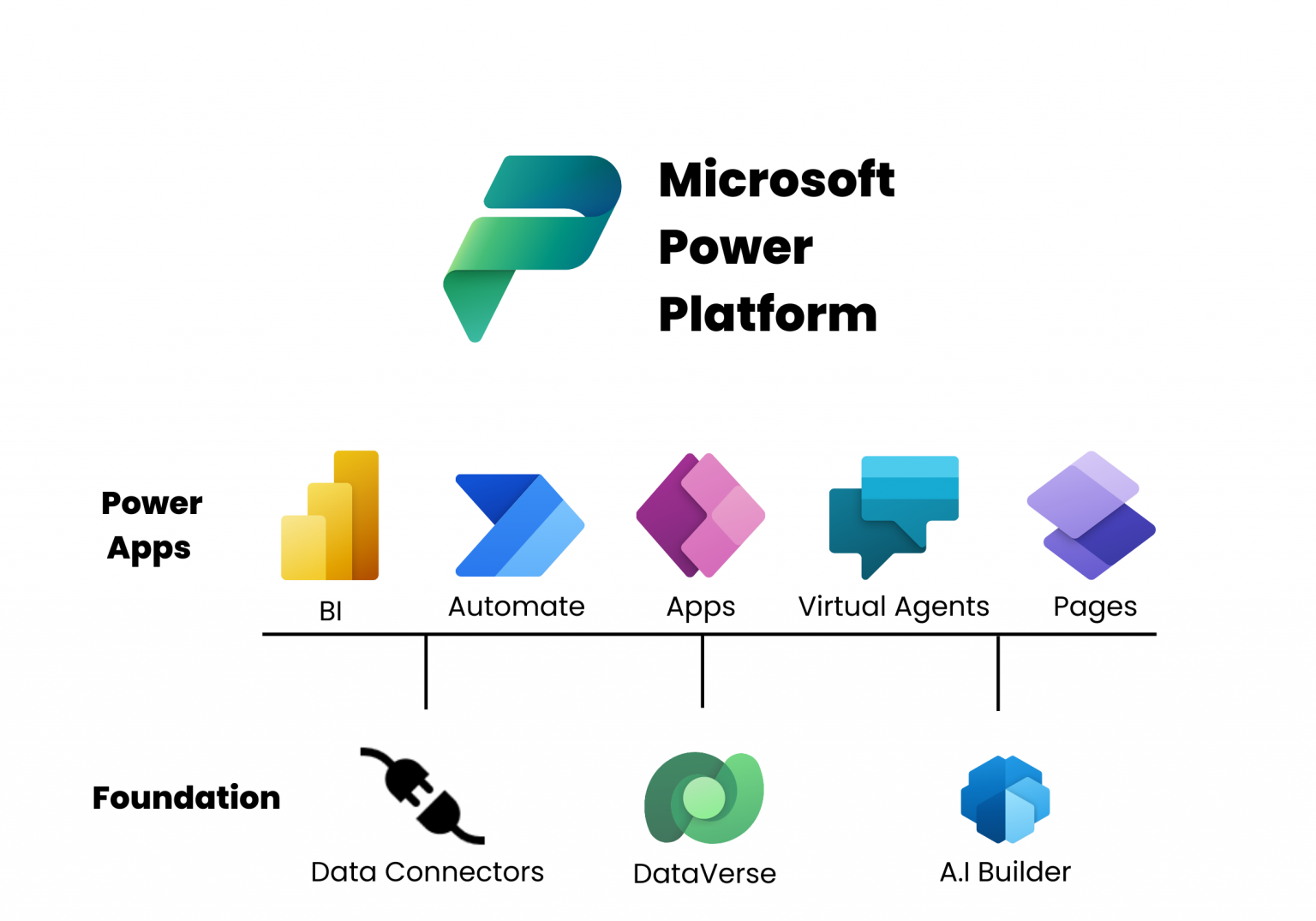
Microsoft’s Security Foundation for Power Platform
Microsoft Power Platform is built on a strong security foundation that aligns with Zero Trust principles, which include:
- Verify Explicitly – Every user and device must undergo continuous verification.
- Use Least Privilege Access – Grant minimal permissions needed to perform a task.
- Assume Breach – Treat every access request as potentially compromised.
Microsoft integrates advanced security solutions to protect Power Platform applications, including:
- Microsoft Defender – Detects and prevents cyberattacks.
- Microsoft Sentinel – Provides security information and event management (SIEM).
- Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) – Manages authentication and access control.
- Microsoft Purview – Ensures compliance and data governance.
- Microsoft Intune – Strengthens endpoint security.
🔗 Learn more about Microsoft’s Security Products: Microsoft Security Center
Power Platform’s Multi-Layered Security Model
Power Platform implements multiple security layers to protect applications and data:
1. Identity & Access Management
- Authentication & Conditional Access – Microsoft Entra ID ensures secure authentication for users and applications.
- Role-Based Security in Dataverse – Restricts data access based on user roles.
- Guest User & External Access Controls – Defines security permissions for third-party collaborators.
2. Data Protection & Encryption
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies – Prevents unauthorized data movement.
- Customer-Managed Encryption Keys – Provides full control over data encryption.
- Microsoft Lockbox – Ensures customer approval before Microsoft personnel access data.
3. Network Security & Compliance
- Tenant Isolation & IP Firewalls – Restricts cross-tenant data access.
- Azure Private Link & ExpressRoute – Secure connections between Power Platform and on-premises resources.
- Web Application Firewall for Power Pages – Protects external-facing websites from cyber threats.
4. Secure Development Lifecycle
- Security by Design – Power Platform follows a structured Security Development Lifecycle (SDL), covering:
- Secure coding practices.
- Automated security testing.
- Vulnerability scanning.
- Penetration testing.
- Continuous monitoring.
🔗 Read about Microsoft’s Security Development Lifecycle: SDL Overview
Best Practices for Power Platform Security
To strengthen Power Platform security, organizations should adopt the following best practices:
✅ Enforce Strong Access Controls – Use Microsoft Entra ID, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access controls (RBAC).
✅ Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policies – Classify sensitive data and restrict unauthorized data movement.
✅ Monitor & Audit Activity Logs – Integrate Power Platform with Microsoft Sentinel for real-time security monitoring.
✅ Secure External Connections – Use Azure Private Link and Virtual Network Data Gateways for connecting to on-premises resources securely.
✅ Apply Zero Trust Security Model – Continuously verify every access request and minimize user privileges.
✅ Train & Educate Users – Ensure that citizen developers understand security best practices and comply with enterprise security policies.